Introduction In our previous blog, we explained the basics of electrolysis and how electricity can drive chemical changes that do not happen on their own. In this post, we will look at one of the simplest and most important examples: the electrolysis of water. This school experiment is a clear …
Common GCSE Chemistry Mistakes: Acids, Bases & Salts Explained
Common GCSE Exam Mistakes (Acids, Bases and Salts) Mistake 1: Confusing Strong and Concentrated Acids (GCSE Chemistry) One of the most common mistakes in GCSE Chemistry is confusing the terms strong and concentrated when describing acids. Although these words sound similar, they mean completely different things and cannot be used …
Acids, Bases and Alkalis Explained (GCSE Chemistry) | pH Scale, Indicators & Salts
Introduction: Acids, Bases and Alkalis What is the first thing that comes to your mind when you think about acids and bases?Most people think about the acid in their stomach or the citric acid in lemons when they hear the word acid. When they think about bases, they often remember …
Energy change (Enthalpy Change) in chemical Reactions
What Is Energy in Molecules? You have already learned about energy in everyday life such as kinetic energy, potential energy, energy needed to do work, energy from food, and many others. These ideas all remind us of one simple point: Energy makes things happen. But in chemistry, we are not …
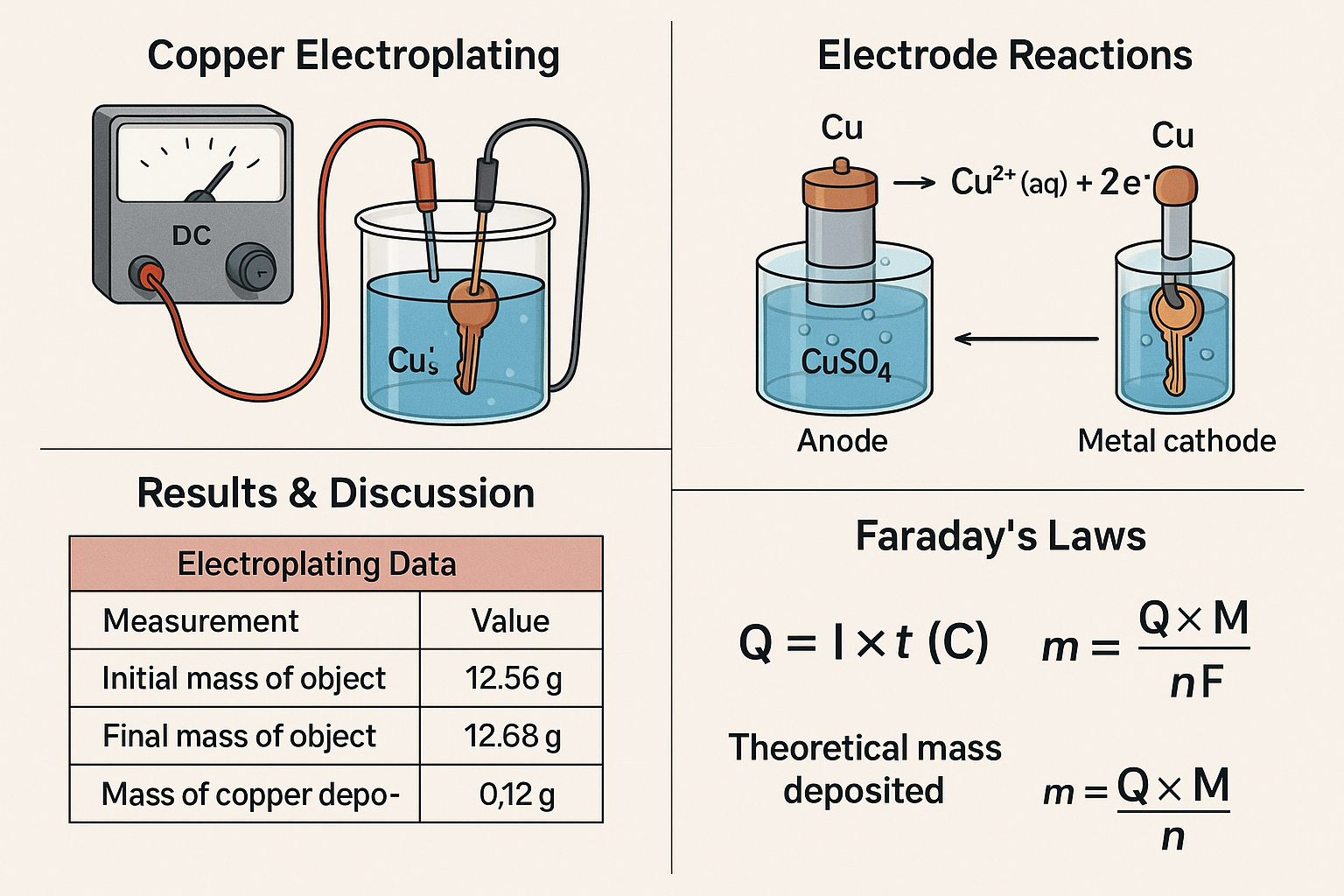
Copper Electroplating Lab Report | Faraday’s Laws & Redox Reactions Explained
Introduction Electroplating is an industrial process that uses electricity to coat the surface of a metal object with a thin layer of another metal. In copper electroplating, a copper anode and a conductive object (the cathode) are placed in a solution containing copper(II) ions. When an electric current is applied, …
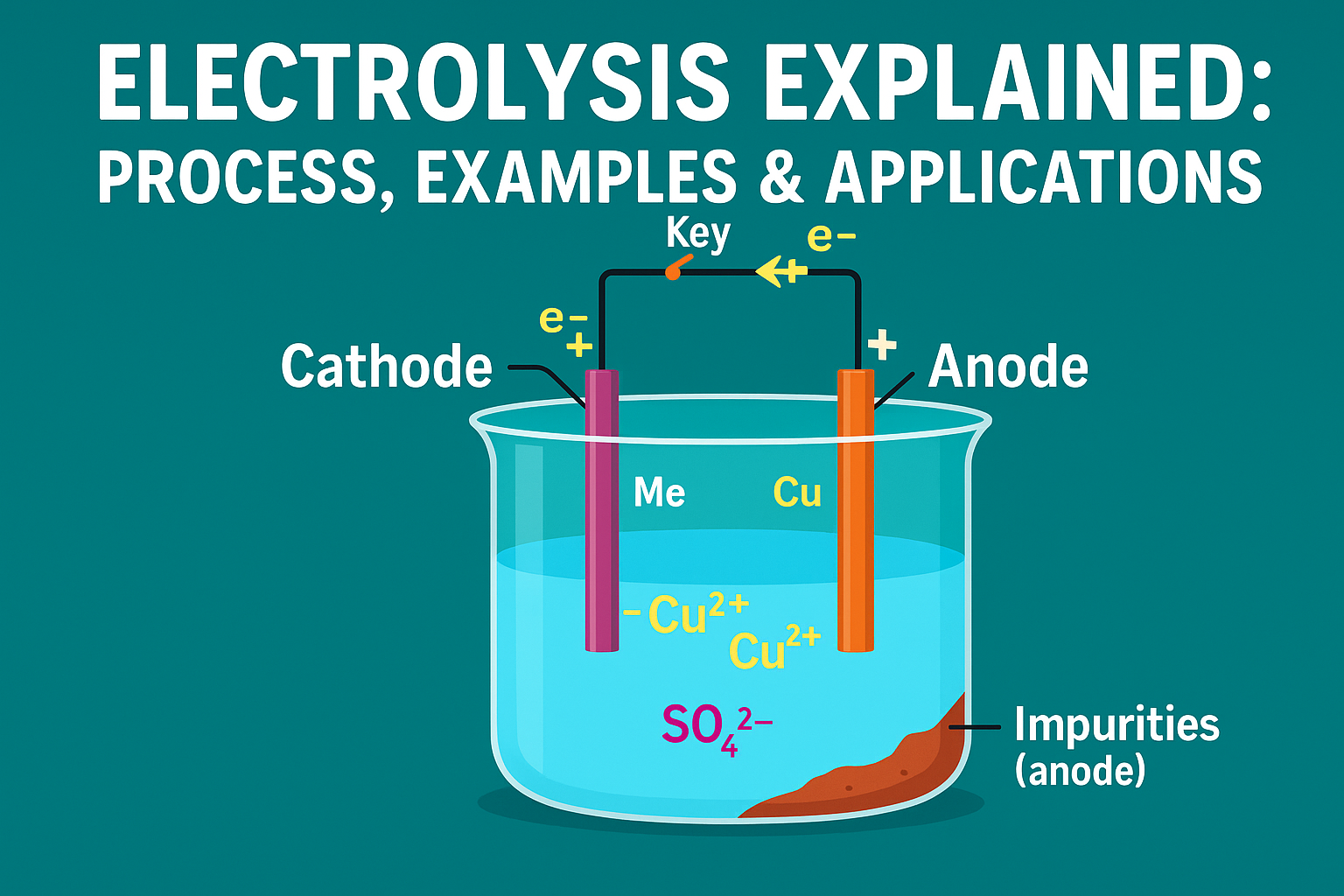
Electrolysis Explained: Process, Examples & Applications
Introduction Have you ever looked at a piece of jewellery and wondered how it got that flawless gold coating? It is not paint, and it is definitely not done with a tiny brush. The secret lies in a process called electrolysis. Electrolysis is where electricity steps in and makes chemical …
Law of Definite Proportions: Discovery, History, Questions
Introduction – Law of Definite Proportions Why does water always behave like water, no matter where it comes from? Why do compounds like carbon dioxide and copper carbonate always form in the same way? Before scientists understood atoms, they were already noticing something strange but consistent. When elements combine to …
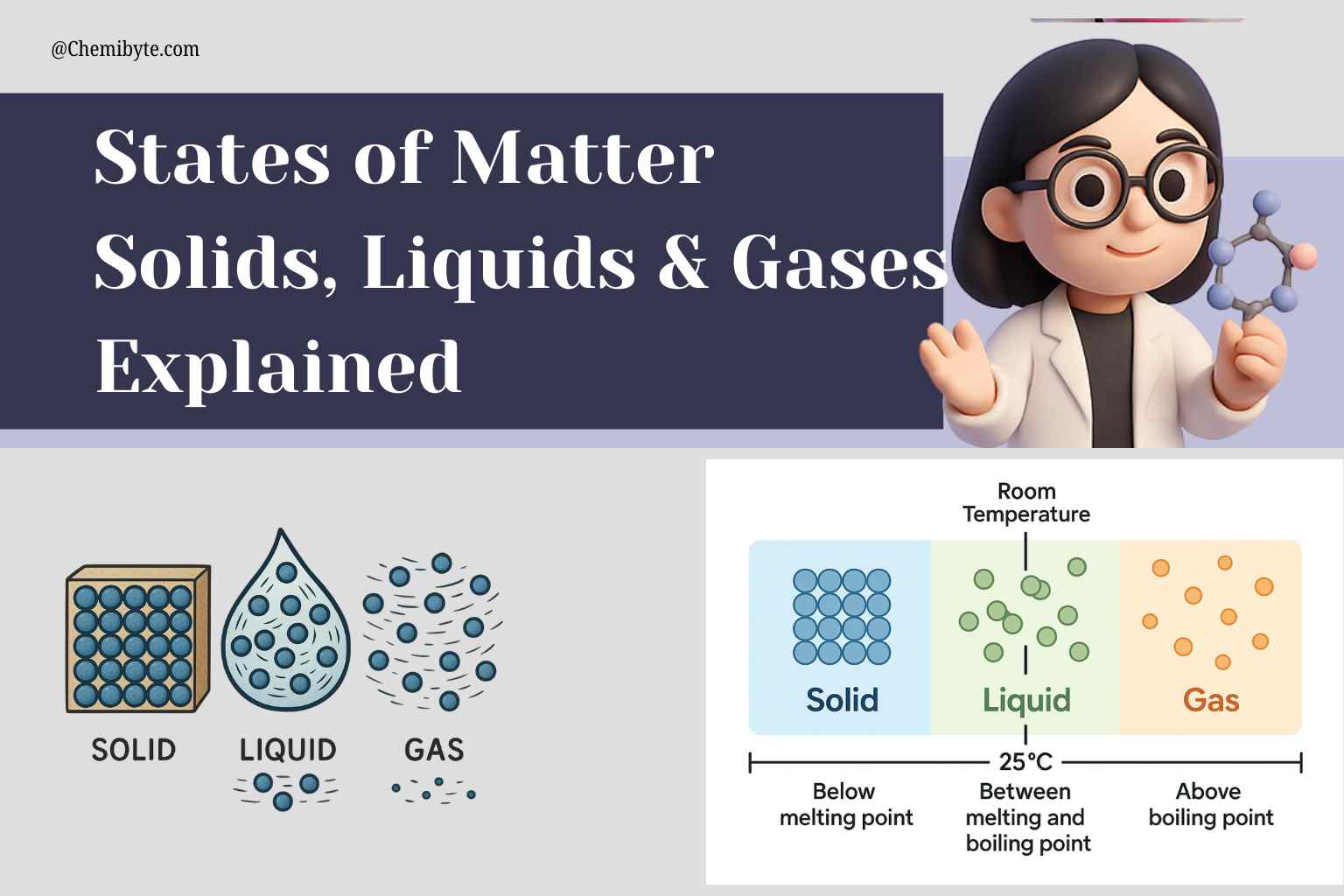
States of Matter – Solids, Liquids & Gases Explained(GCSE )
Introduction:States of Matter Everything around us air, water, metal, or even plastic is made of something called matter. But matter doesn’t always look or act the same way. Why? Because it can exist in different forms called “states.” This is one of the first big ideas you learn in chemistry: …
How Did Scientists First Discover That Water Is Made of Hydrogen and Oxygen?
Introduction- How Did Scientists First Discover That Water Is Made of Hydrogen and Oxygen? How scientists discovered water is made of hydrogen and oxygen is one of the most fascinating stories in chemistry history. Before this discovery, people believed water was a basic element. In our previous post on atomic …
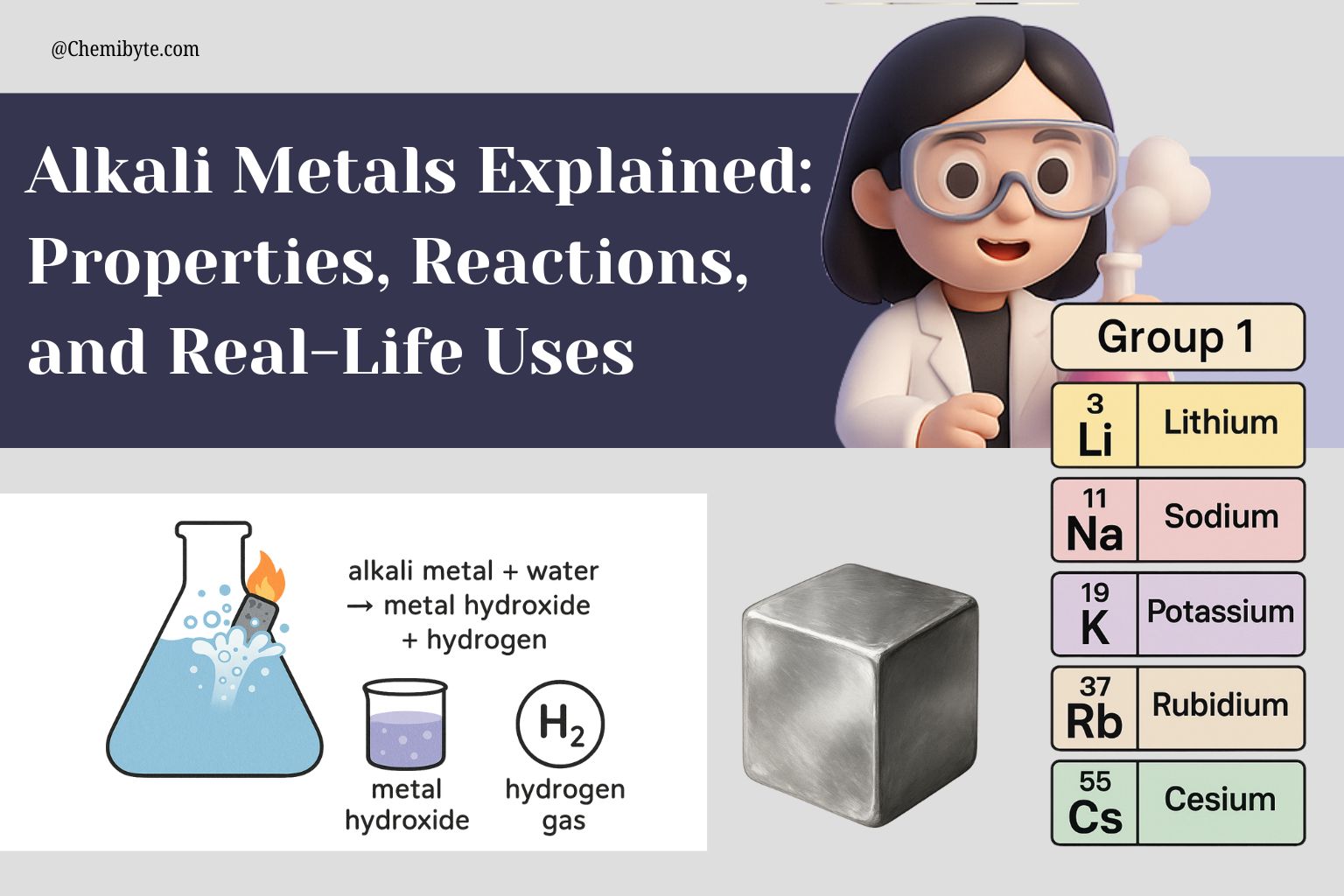
Alkali Metals Explained: Properties, Reactions, and Real-Life Uses (GCSE Chemistry Guide)
Alkali Metals Explained: Properties, Reactions, and Real-Life Uses Have you ever wondered — what are alkali metals? When you think about metals, names like iron, steel, or aluminium probably come to mind. These are strong, shiny materials we see in buildings, tools, and everyday objects. But there’s another group of …